Python Code for Software Licensing
How do you create license keys for software in Python? Well, setting up a Python license key system is effortless with Cryptolens. Instead of coding your own solution from scratch, we have detailed guides and SDKs so you can set up key verification and protect your Python code. If you want to read more about the code-it-yourself VS outsourcing route, please read this blog post.
We have also made the following YouTube video that goes into detail about how you implement a Python license key manager:
Creating License Keys for a Python Application
A software license management solution has to establish a lock in your software code that only allows entry to people who put in a valid digital license key. If the key is invalid, or if they are unable to insert a key, the system should deny entry to the application. Without this system in place, anyone can access your software app, and it becomes very difficult to sell such a product. That is why a software licensing solution is important when protecting your code against unauthorized users.
A Licensing as a Service (LaaS) provider such as Cryptolens allows you to set up a license manager for Python within minutes that performs full key verification. This enables quicker software license implementation and you gain access to all of the advanced licensing techniques you will need, such as usage-based pricing, offline license verification, floating and node-locked licenses, and user-account-based licensing.
Implementing a Python License Key System
Getting started with a cloud-based software license manager such as Cryptolens can be done by following 3 easy steps:
1. Install our Python SDK.
2. Create a free Cryptolens account.
3. Insert a code snippet into your code
1. Let us begin with the SDK. Cryptolens offers comprehensive SDKs in your favorite programming languages, including Python, to make it effortless to implement a Licensing as a Service (LaaS) platform within minutes. Install our Python SDK here.
2. Create a free Cryptolens account to get access to our easy-to-use dashboard where you can create and manage license keys and restrictions. You can also find your access tokens and other parameters that you have to insert into your code. Cryptolens offers you a way to implement licensing for free at your own pace, and you only have to pay when you get customers of your own. Check out our pricing plans here, and you can always get started for free.
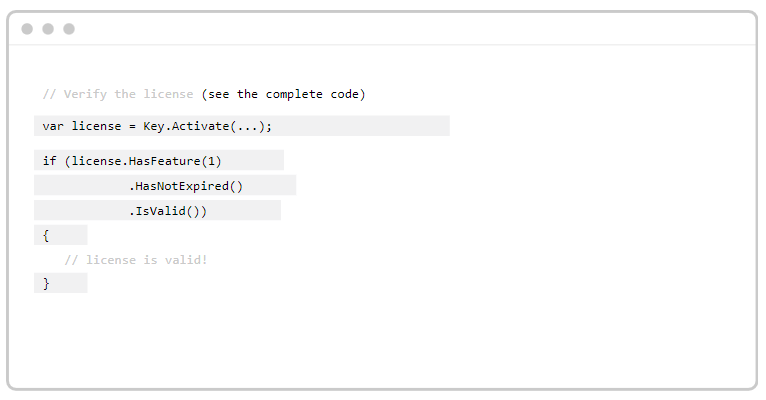
3. The last step for implementing a Python license key system is to insert a code snippet into your application’s code. We provide comprehensive help guides to make the implementation seem effortless. See the full code snippet in your programming language here. This is an overview of what the Python code snippet looks like:
from licensing.helpers import Helpers
from licensing.models import Response, RSAPublicKey
from licensing.methods import Key
pubKey = "<RSAKeyValue><Modulus>sGbvxwdlDbqFXOMlVUnAF5ew0t0WpPW7rFpI5jHQOFkht/326dvh7t74RYeMpjy357NljouhpTLA3a6idnn4j6c3jmPWBkjZndGsPL4Bqm+fwE48nKpGPjkj4q/yzT4tHXBTyvaBjA8bVoCTnu+LiC4XEaLZRThGzIn5KQXKCigg6tQRy0GXE13XYFVz/x1mjFbT9/7dS8p85n8BuwlY5JvuBIQkKhuCNFfrUxBWyu87CFnXWjIupCD2VO/GbxaCvzrRjLZjAngLCMtZbYBALksqGPgTUN7ZM24XbPWyLtKPaXF2i4XRR9u6eTj5BfnLbKAU5PIVfjIS+vNYYogteQ==</Modulus><Exponent>AQAB</Exponent></RSAKeyValue>"
res = Key.activate(token="WyIyNTU1IiwiRjdZZTB4RmtuTVcrQlNqcSszbmFMMHB3aWFJTlBsWW1Mbm9raVFyRyJd",\
rsa_pub_key=pubKey,\
product_id=3349, key="ICVLD-VVSZR-ZTICT-YKGXL", machine_code="test")
if res[0] == None:
print("An error occured: {0}".format(res[1]))
else:
print("Success")